DH Gagne, CC Steele, J Keating, K Bradbury, A Badhwar, SF Elahi. Preliminary Study of Yucatan Porcine Breast Morphology: Identifying Basic Differences and Similarities for Surgical Model Applications.
Background/Objectives: The porcine mammary anatomy is poorly characterized, and structures are difficult to differentiate macroscopically, unlike human mammary tissue. The objective of this exploratory study was to describe the Yucatan porcine breast tissue morphology and identify the basic differences and similarities to human breast tissue.
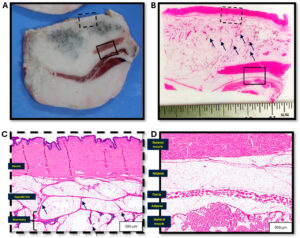 Methods: Samples from an adult, non-parous female Yucatan pig were prepared utilizing various methods: freezing at −80 °F (−26.67 °C) with a thickness of 0.5 cm/post-fixation in formalin; freezing at −20 °F (−6.67 °C) with a thickness of 0.5 cm/post-fixation in formalin; or formalin fixed and incised at ~0.8 cm. A descriptive comparison of the gross and microscopic images of the porcine breast morphology to the previously described human breast anatomy was performed.
Methods: Samples from an adult, non-parous female Yucatan pig were prepared utilizing various methods: freezing at −80 °F (−26.67 °C) with a thickness of 0.5 cm/post-fixation in formalin; freezing at −20 °F (−6.67 °C) with a thickness of 0.5 cm/post-fixation in formalin; or formalin fixed and incised at ~0.8 cm. A descriptive comparison of the gross and microscopic images of the porcine breast morphology to the previously described human breast anatomy was performed.
Results: As examined grossly, frozen sections allowed narrower serial cross-sectioning and better visualization of the structures and relationships. The mammary glands were poorly demarcated with extensive interspersed adipose tissue throughout the periphery. The mammary tissue appeared grossly as pigmented tissue and extended within ~0.5 cm from the skin surface, ~2.0 cm deep (within ~0.5 cm of the deep muscle layer), and ~6.5 cm laterally (centered on a teat). There were a number of similarities between Yucatan porcine and human breast tissue, yet there were several inherent structural differences. In contrast to human mammary tissue, porcine mammary glands consist of more diffuse acinar tissue, less well demarcated by defined fascial, lamellar, and ligamentous structures.
Conclusions: The Yucatan porcine mammary morphology and similarities to the human mammary region allow for the use of this animal model to guide those developing relevant technologies or performing local surgical interventions in the preclinical setting.

